The 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry has been awarded to Moungi Bawendi of the Massachusetts Institute of Expertise, Louis Brus of Columbia College, and Alexei Ekimov of Nanocrystals Expertise Inc. “for the invention and synthesis of quantum dots.” The properties of those nanoparticles similar to colour and thermal traits change with their measurement.
“These achievements signify an essential milestone in nanotechnology. And in the present day, there are quite a few functions of quantum dots, starting from QLED screens to imaging in biochemistry and drugs, and far more,” mentioned Johan Åqvist, a biochemist at Uppsala College and chair of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry, on the press convention.
As early because the 1930s, researchers like physicist Herbert Fröhlich on the College of Bristol had predicted the weird properties of nanoparticles, however for a few years, researchers have been unable to check them. “For the subsequent 5 a long time, it appeared practically unimaginable to make such supplies,” mentioned Heiner Linke, a nanoscience researcher at Lund College and member of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry, on the press convention.
See additionally “Nobel Prize for mRNA Vaccines”
In 1981, nevertheless, Ekimov, working on the S. I. Vavilov State Optical Institute within the former Soviet Union, made a groundbreaking discovery by measuring the sunshine absorption of coloured glass.1 On the time, scientists knew that including a single substance to glass might lead to completely different colours of glass, relying on how the fabric was heated and cooled. Ekimov used copper chloride to paint glass by heating the glass to completely different temperatures and cooling it for various lengths of time. This produced tiny copper chloride crystals of various sizes. When he measured the sunshine absorption of the glass, he discovered that the dimensions of the particles affected their gentle absorption; smaller particles absorbed bluer gentle. Ekimov realized that he had demonstrated a size-dependent quantum impact, and though he printed his findings in a Soviet analysis journal, his analysis was troublesome to entry in the USA.
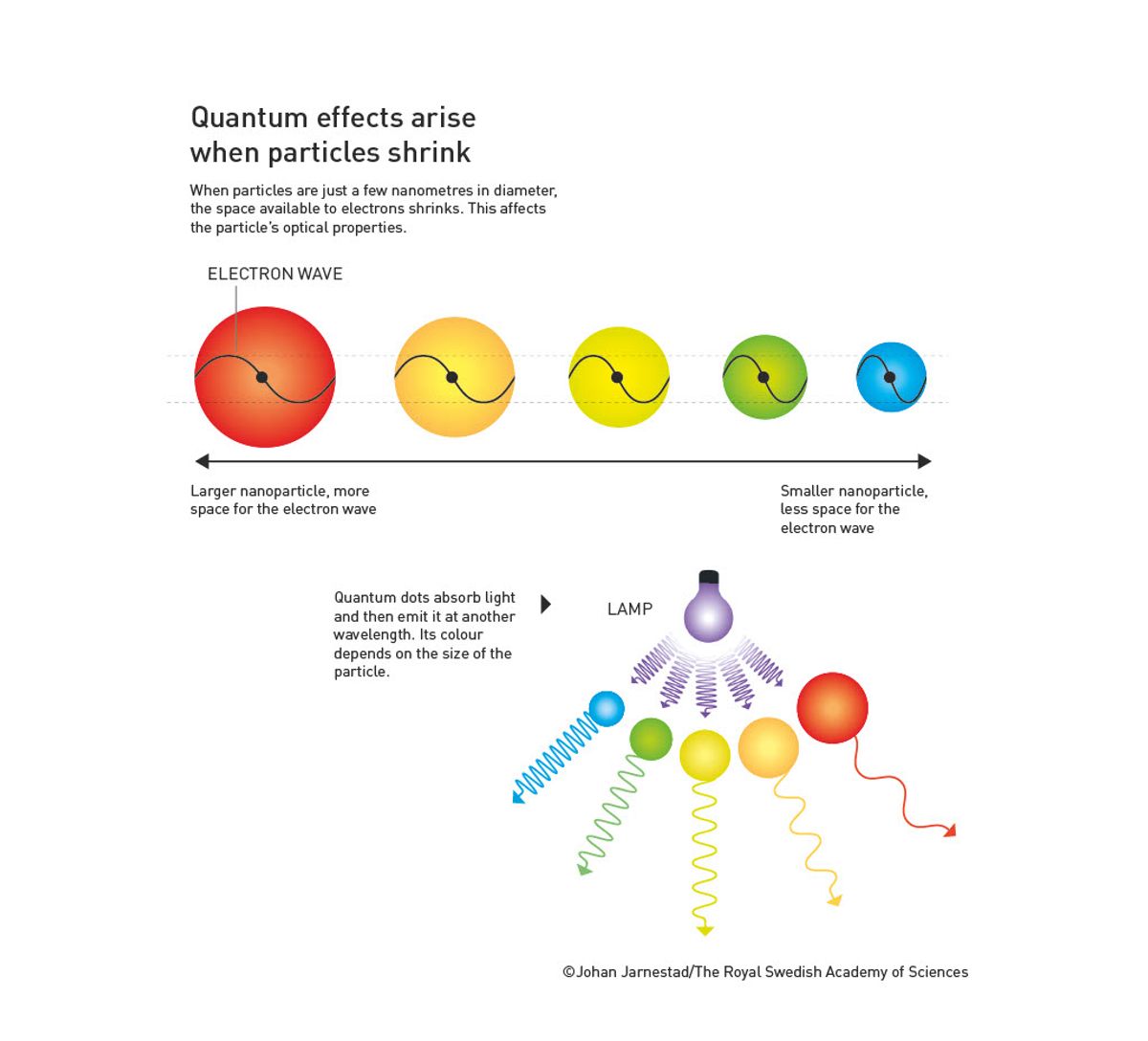
The properties of quantum dots, together with colour, change with their measurement.
© Johan Jarnestad/The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
See additionally “Biocompatible Reactions In Living Cells Garner Chemistry Nobel”
Unaware of Ekimov’s analysis, Brus, working at Bell Laboratories in the USA on the time, independently produced quantum dots of his personal two years later.2 Brus experimented with tiny particles of cadmium sulfide for his work on utilizing photo voltaic vitality to drive chemical reactions. He seen that the optical properties of those particles modified over time, and hypothesized that it was as a result of the particles have been rising bigger. He then in contrast particles of various sizes and noticed the identical size-dependent quantum impact, turning into the primary particular person to find quantum dots in answer.
“Nonetheless,” mentioned Åqvist, “for these quantum dots to grow to be actually helpful, [scientists] wanted to have the ability to make them in answer with beautiful management of their measurement and floor. Moungi Bawendi invented an ingenious chemical methodology for doing simply this. He might now make good nanoparticles of very particular measurement and really prime quality.” Bawendi’s exact synthesis method, printed in 1993, enabled the broader industrial use of quantum dots.3
Whereas quantum dots aren’t but extensively utilized in biomedicine, they’ve many potential functions, together with imaging of dwelling cells and tumors, phototherapy for most cancers, and traceable drug supply.4 Quantum dots are nonetheless an lively space of analysis and, mentioned Linke, “we imagine that the actually massive functions are nonetheless sooner or later.”
References
- Ekimov AI, Onushchenko AA. Quantum size effect in three-dimensional microscopic semiconductor crystals. Soviet Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics Letters. 1981;34:345.
- Rossetti R et al. Quantum size effects in the redox potentials, resonance Raman spectra, and electronic spectra of CdS crystallites in aqueous solution. The Journal of Chemical Physics. 1983;79(2):1086-1088.
- Murray CB et al. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(19):8706-8715.
- Abdellatif AAH et al. Biomedical Applications of Quantum Dots: Overview, Challenges, and Clinical Potential. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1951-1970.