Imperceptible to us, crops are surrounded by a fine mist of airborne compounds that they use to speak and defend themselves. Sort of like smells, these compounds repel hungry herbivores and warn neighboring crops of incoming assailants.
Scientists have identified about these plant defenses for the reason that 1980s, detecting them in over 80 plant species since then. Extra lately, a workforce of Japanese researchers deployed real-time imaging strategies to disclose how crops obtain and reply to those aerial alarms.
This was a giant hole in our understanding of plant chatter: We knew how crops ship messages, however not how they obtain them.
Within the examine, printed final 12 months, Yuri Aratani and Takuya Uemura, molecular biologists at Saitama College in Japan, and colleagues rigged up a pump to switch compounds emitted by injured and insect-riddled crops onto their undamaged neighbors, and a fluorescence microscope to observe what occurred.
frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
Caterpillars (Spodoptera litura) had been set upon leaves reduce from tomato crops and Arabidopsis thaliana, a standard weed within the mustard household, and the researchers imaged the responses of a second, intact, insect-free Arabidopsis plant to these hazard cues.
These crops weren’t any atypical weeds: They’d been genetically altered so their cells contained a biosensor that fluoresced inexperienced when an inflow of calcium ions was detected. Calcium signaling is one thing human cells use to speak too.
The workforce used an analogous approach to measure calcium indicators in a examine final 12 months of fluorescent Mimosa pudica crops, which quickly move their leaves in response to the touch, to keep away from predators.
This time, the workforce visualized how crops responded to being bathed in risky compounds, which crops launch inside seconds of wounding.
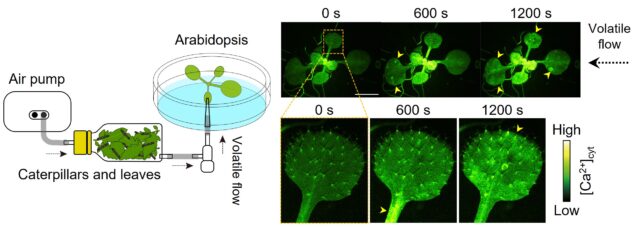
It wasn’t a pure set-up; The compounds had been concentrated in a plastic bottle and pumped onto the recipient plant at a relentless charge, however this allowed the researchers to research what compounds had been within the pungent combine.
As you possibly can see within the video above, the undamaged crops acquired the messages of their injured neighbors loud and clear, responding with bursts of calcium signaling that rippled throughout their outstretched leaves.
Analyzing the airborne compounds, the researchers discovered that two compounds known as Z-3-HAL and E-2-HAL induced calcium indicators in Arabidopsis.
Additionally they recognized which cells are the primary to answer the hazard cues by engineering Arabidopsis crops with fluorescent sensors completely in guard, mesophyll, or epidermal cells.
Guard cells are bean-shaped cells on plant surfaces that type stomata, small pores that confide in the ambiance when crops ‘breathe’ in CO2. Mesophyll cells are the inside tissue of leaves, and epidermal cells are the outermost layer or pores and skin of plant leaves.
When Arabidopsis crops had been uncovered to Z-3-HAL, guard cells generated calcium indicators inside a minute or so, after which mesophyll cells picked up the message.
What’s extra, pre-treating crops with a phytohormone that shuts stomata considerably diminished calcium signaling, suggesting stomata act because the ‘nostrils’ of the plant.
“We’ve got lastly unveiled the intricate story of when, the place, and the way crops reply to airborne ‘warning messages’ from their threatened neighbors,” Masatsugu Toyota, a molecular biologist at Saitama College in Japan and senior writer of the examine, explained when the examine was printed.
“This ethereal communication community, hidden from our view, performs a pivotal position in safeguarding neighboring crops from imminent threats in a well timed method.”
The examine has been printed in Nature Communications.
An earlier model of this text was printed in January 2024.




